Webinar | Industry insights | Nonprofits & associations | Financial management
Nonprofit Financial Management: Overview and Best Practices
May 17, 2023
|
Nonprofits have unique accounting practices, compliance requirements, and reporting responsibilities. An effective nonprofit financial management plan helps fulfill those obligations while promoting sustainability and building stakeholder trust. This article covers the basics of nonprofit financial management and provides best practices to help upgrade your strategy and ensure mission success.
Components of Nonprofit Financial Management
Nonprofit financial management is a set of practices that ensure efficient governance of an organization’s financial resources. Some components of an effective financial management plan include:
Fundraising and Donor Management
Most nonprofits depend on donors to fund program activities. That’s why it’s essential to implement strategies to generate revenue, build donor relationships, and improve the organization’s financial position.
Grant Management
Grants typically have restrictions, including funding for a specific purpose, geographic and time constraints, prohibition from political activities, and reporting requirements. Complying with these restrictions requires implementing processes that ensure nonprofits use money according to the terms of these agreements.
Budgeting and financial planning
Resource planning is critical to an organization’s ability to improve its financial capacity and maintain long-term sustainability. Therefore, developing and maintaining a monthly and annual budget is essential to ensure that funds cover administrative expenses, program delivery, fundraising, and marketing activities.
Cash Flow Management
Steady cash flow is critical to fund current and future programs. As a result, nonprofits should create a cost-effective plan to ensure that programs receive adequate funding while covering functional expenses.
Financial Reporting
Nonprofits must maintain accurate financial records and produce reports that adequately inform the decision-making process. Besides providing transparency, publishing nonprofit financial statements to high standards demonstrates accountability to board members, executive directors, donors, and other stakeholders.
Compliance
Nonprofits must comply with requirements set by government agencies, regulators, and funding organizations. As a result, nonprofits must develop procedures to comply with all regulations, laws, and internal policies governing operations.
Factors That Make Nonprofit Financial Management Unique
Upgrading your nonprofit financial management strategy is a significant undertaking. Unfortunately, most business advice, education, and software tools revolve around the needs of regular businesses.
That’s why it’s essential to clarify how nonprofit financial management differs before upgrading your strategy.
Some key differences include:
Nonprofits operate with unique internal controls, procedures, and processes.
Most nonprofits operate with donor and grant money. Strong internal controls are therefore required to ensure adequate fund management and risk mitigation. Further, robust internal controls demonstrate increased accountability and help build trust with stakeholders, donors, and the public. Examples include well-defined policies and procedures, separation of duties, consistent monitoring, and regular reporting of financial information to stakeholders.
Nonprofits monitor and report financial activity under different accounting guidelines.
Nonprofits have a tax-exempt status, and are therefore subjected to alternative rules and regulations set by government agencies and regulatory bodies. As a result, they must follow separate accounting rules such as the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Accounting standards set by the FASB or IFRS typically affect nonprofit financial operations in several areas, including:
- Revenue recognition
- Expense allocation
- Reporting requirements
- Net asset classification
- Disclosure requirements
- Annual IRS Form 990 filings
Audits, reporting, and compliance are critical components of nonprofit financial management.
Since nonprofits operate in a different legal and financial regulatory framework, they must comply with industry-specific regulations, tax laws, and reporting requirements. Further, nonprofit organizations must undergo periodic audits by regulatory bodies such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Audits are also mandatory for some grant agreements or other funding arrangements. As a result, nonprofit financial management must emphasize transparency and accountability in order to comply with regulatory requirements.
Role of the Finance Committee
The nonprofit finance committee is vital to a nonprofit organization’s leadership structure.
Typical responsibilities of the finance committee include:
- Budget approvals
- Financial statement monitoring
- Financial reporting
- Investment decisions
A qualified and well-organized finance committee is critical to a successful nonprofit financial management strategy. Ensure your team has a complementary mix of skills, education, and experience in all areas of financial management. This ensures programs are funded appropriately in accordance with the organization’s mission.
7 Best Practices to Upgrade Your Nonprofit Financial Management Strategy
Some standard best practices for nonprofit financial management include developing and maintaining budgets, staff training, and consistent program monitoring.
Some strategic best practices that go above and beyond these basic guidelines include:
Best Practice #1: Implement appropriate checks and balances.
A robust checks and balances strategy prevents fraud and fund mismanagement. Other benefits include increased transparency, accountability, and trust within the organization.
Best Practice #2: Automate processes to streamline operations across the organization.
Automating processes using dedicated software helps nonprofits reduce administrative and program expenses, save time, increase efficiency, and improve accuracy. Further, software automation enables better data management to help finance teams quickly produce reports on grants and other program activities.
Best Practice #3: Monitor financial performance against the most relevant metrics and KPIs.
There are hundreds of nonprofit financial metrics you can track to measure performance and financial health. Choosing the right metrics is the key to effectively gauging the success of your financial management practices, nonprofit programs, and overall organizational strategy.
Best Practice #4: Use financial software customized for nonprofits.
Customized nonprofit accounting software provides specific features critical to nonprofit financial management, including fund accounting and grant management. Dedicated software also offers tools to track donations, produce reports for specific compliance requirements, track budgets to actuals, flag reimbursable expenses upon entry, and more.
Best Practice #5: Implement strong internal controls to safeguard assets.
Establish robust internal controls to protect your organization’s assets and prevent fraud. Typical measures include process automation, establishing checks and balances, and implementing accounting procedures that track income and expenses by program or activity.
Best Practice #6: Review your budget periodically.
The economy is always in a state of flux. That’s why it’s essential to use budgeting software that tracks progress in real time and provides dashboards that reveal your organization’s current financial state. Besides providing powerful insights, software powered by real-time data helps managers implement critical changes that align with current economic conditions.
Best Practice #7: Integrate software systems to improve efficiency and accuracy.
Cloud-based financial software connects to your other systems to improve data management, minimize data entry, reduce errors, and streamline overall financial operations. Integrated software also leverages real-time data to provide accurate, timely insights and enhances collaboration across your entire team. Examples include payment processing systems, membership management software, and learning management systems.
Effective nonprofit financial management ensures mission success.
Investing in the right software and digital tools improves nonprofit financial management and positively impacts your nonprofit’s mission. enSYNC helps leading nonprofits reach their maximum potential with powerful solutions that improve productivity, enhance efficiency, and unlock the power of data-driven decision-making.
Contact us to schedule a free assessment to learn more.
Recent Posts
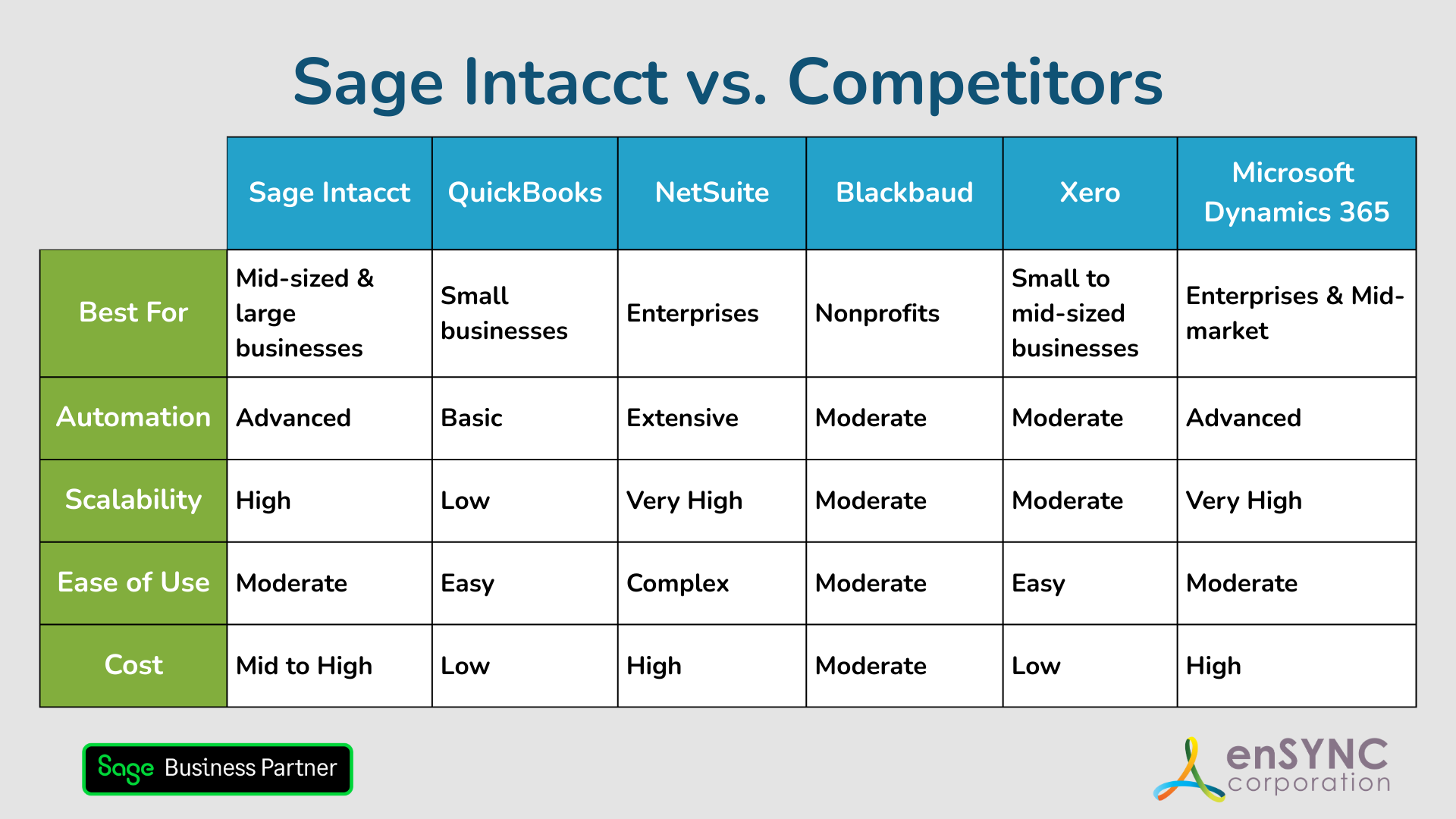
Sage Intacct vs. Competitors: Finding the Best Accounting Solution for Your Nonprofit
Choosing the right accounting software is a critical step for any organization — and a deeply personal one, too. How to choose the accounting...

How Sage Intacct Transforms Nonprofit Financial Management: A Complete Guide
Staying on top of financial management is crucial for all businesses, especially nonprofits. Nonprofits often have limited resources and handle...
Enjoying our blog?
At enSYNC, we want to empower associations and nonprofits to make well-educated decisions. If you want our industry knowledge (and other free guides) sent directly to your inbox, fill out the form below.


